The full name of mineral powder among the three primary adhesive materials for concrete is granulated blast furnace slag powder, which is obtained when pig iron is smelted in a blast furnace (steel-making is called steel slag). It is a melt with silicates and aluminosilicates as its main components. It is a fine particle formed by water quenching and rapid cooling at high temperatures without enough time to crystallize a glassy substance.

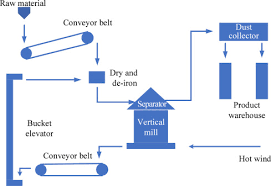
1. Production Process of Slag Powder
In the blast furnace ironmaking process, in addition to iron ore and fuel (coke), an appropriate amount of limestone and dolomite are also added as cosolvents to lower the smelting temperature. The calcium oxide, magnesium oxide, and goaf in the iron ore and the ash phase in the coke obtained by decomposing them in the blast furnace are melted to generate a molten substance with silicates and aluminosilicates as the main components. The surface of molten iron is regularly discharged from the slag discharge port and is rapidly cooled by air or water to form granular particles, which are slag. Slag contains more than 95% of the glass and minerals such as dicalcium silicate, feldspar, and wollastonite, which are close to the composition of cement. If the slag is not quenched, its mineral form is a stable crystal. Only a tiny portion of dicalcium silicate has a specific hydration activity. It can be understood here that a certain amount of energy is “sealed” into the slag through water quenching and rapid cooling treatment. This activity can be stimulated under alkaline conditions. The higher the slag discharge temperature and the faster the cooling rate, the greater the potential chemical energy of vitrified slag. 0.3-1 ton of slag must be discharged for every pig iron produced. The slag cooled by water quenching is then subjected to a grinding process to obtain the slag used in the mixing station.
2. Performance and Application of Slag Powder
Replacing a certain proportion of clinker or cement with mineral powder can produce a “volcano ash effect” and a “micro-aggregate effect,” thus making various raw materials complementary in performance. Not only can it effectively dispose of waste residue produced by steel plants, but it can also reduce the production cost of cement or concrete.
2.1 Characteristics of Slag Poweder
Slag micron powder has potential hydration activity. When mixed with cement, the calcium hydroxide produced by cement hydration can stimulate potentially active mineral powder. The mineral powder can undergo a hydration reaction to generate hydrated calcium silicate, which can be filled in the pores of cement concrete, greatly increasing its density and converting lower-strength calcium hydroxide crystals into higher-strength hydrated silicon gel.
2.2 Effect of chemical components in slag on activity
Calcium oxide is an alkaline oxide and is the main chemical component of slag, generally accounting for about 40%. It exists in silicates in slag, such as dicalcium silicate, which is active. Therefore, calcium oxide is the main factor that determines the activity of slag. The higher its content, the greater the activity of slag.
Alumina is an acidic oxide and is the better active ingredient in slag. It exists in the form of aluminate or aluminosilicate in slag. The alumina content is generally 5-15% but may be as high as 30%. Silicon oxide is slightly acidic, and its slag content is about 30-40%. It makes slag less active than calcium oxide and aluminum oxide.
Magnesium oxide is less active than calcium oxide, and its content is generally between 1% and 18%. It appears as a stable compound or glass body in slag and will not cause instability and adverse phenomena. Therefore, magnesium oxide is generally regarded as the active component of slag.
Manganous oxide is harmless to cement stability, but it has a certain impact on slag activity. Its content should be controlled at 1%- 3%. If it exceeds 4%- 5%, slag activity will be significantly reduced.

2.3 Uses of Slag Powder
Mixed with Portland cement in proportion, it can produce high-performance slag cement. Mineral powder with a fineness of 400-450㎡/Kg can be configured with 425 and 425R ordinary Portland cement; as an admixture for concrete, it can improve concrete quality, strength, and durability.
2.4 Effect of Slag Powder
•Can effectively improve the seawater erosion resistance of concrete, especially suitable for seawater projects;
•Can significantly reduce the heat of hydration of concrete and is suitable for configuring large volumes of concrete;
•Can effectively inhibit the alkali-aggregate reaction of concrete and improve the durability of concrete;
•Can significantly reduce the bleeding problem of concrete and improve the workability of concrete;
•Can significantly improve the strength of concrete;
•Can increase the density of concrete and improve the impermeability of concrete;
•Can reduce the cost of concrete.
•Slag quality testing

Leave a comment